Fume Hood Testing Procedures
Health and Safety calibrates all chemical and radiological fume hoods on the main campus, as well as those located at the Biological Field Station, to ensure that they are operating within the parameters recommended for the types of hazardous materials used. Calibration is the measurement and determination of both the minimum and the total airflow capabilities of the fume hood. Based upon the measurements, the performance of the hood is rated based upon the following generally accepted criteria:
| Class 0: Average minimum flow rate of less than 75 feet per minute (FPM). This hood is unsafe for use with hazardous chemicals and radioactive materials. It is acceptable ONLY for nonhazardous materials and nuisance odors. |
| Class 1: Average flow rate of between 75 and 100 FPM. This hood is unsafe for use with hazardous chemicals and radioactive materials. It is acceptable ONLY for nonhazardous materials, nuisance odors, and heat dissipation, |
| Class 2: Average flow rate of at least 100 FPM, and no single point less than 75 FPM. This hood is appropriate for general laboratory usage and most low level radioactive materials. |
| Class 3: Average flow rate of 150 FPM. This hood is usually recommended or required when working with materials that have moderately toxic or radioactive characteristics. |
| Class 4: Average flow rate greater than 200 FPM. This hood is required when working with highly toxic and highly radioactive materials. |
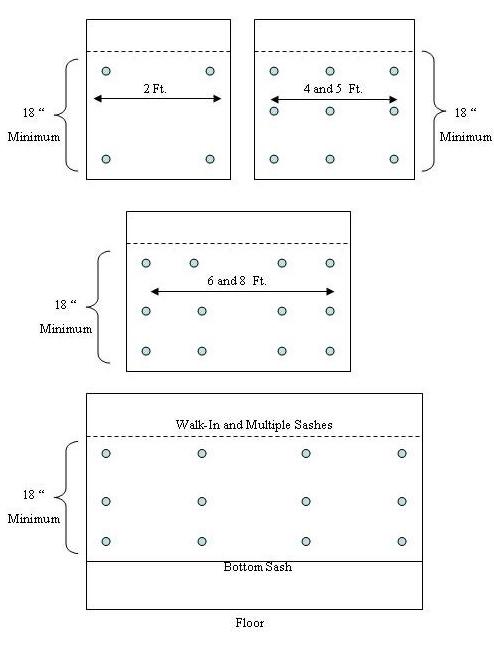
Specific criteria for checking a hood is based upon the design features as well as the size of the hood. Generalized testing points for several sizes and configurations are indicated by diagrams below.
All hoods with movable a sash are tested with a minimum opening of 18″.
Hoods with a 2 ft. wide sash and a constant flow motor are checked with a digital anemometer at 4 points-2″ from the top and both sides, and 2″ from the bottom and both sides.
Hoods with 4 and 5 ft widths and constant flow motors are checked with a digital anemometer at 9 points-2″ from the top and both sides, 2″ from the bottom and both sides, halfway from top to bottom 2″ from both sides, and in the center at the top, middle, and bottom.
Hoods with 6 and 8 ft wide sashes and constant flow motors are checked with a digital anemometer at 12 points-2″ from the top and both sides, 2″ from the bottom and both sides, halfway from top to bottom 2″ from both sides, 1/3 of the distance from each side at a point 2″ from the top, 2″ from the bottom, and halfway from top to bottom at each 1/3 distance.
Hoods with variable flow motors are checked the same as those above, but the height is set at the manufacturer’s installed stops.
Hoods with split sashes have both sashes set at the stops.
Walk in hoods are checked with the bottom sash completely closed, and the top sash set to the standard height, and checked at the corresponding width of the hood.
Walk in hoods with multiple doors are checked with all bottom sashes and all but one upper sash down. The open sash is set to the proper height and checked at the corresponding width locations.
During calibration of the hood, the operator will record the unique hood ID number, the test date, measured flow rate from each test point and the calculated Class on an inspection report sheet. An identification label is dated and affixed to the hood faceplate, including a unique hood ID number, inspection date and Class. Calibration testing information, including recorded flow test rates, is entered into a Departmental database. The original records are filed in accordance with the Departmental Records Retention Policy.